About Hauynite
For Rene Just Hauyn (1743-1822) French crystallographer and mineralogist.
Hauynite hand-specimen
Formula: Na3Ca(Si3Al3)O12(SO4)
System: Cubic (Isometric)
Color: Blue, white, grey
Lustre: Vitreous, Greasy
Hardness: 5½–6
Density: 2.44–2.5
System: Cubic (Isometric)
Color: Blue, white, grey
Lustre: Vitreous, Greasy
Hardness: 5½–6
Density: 2.44–2.5
Hauynite PPL properties
Relief: Low negative
Habit/Form: Crystals are dodecahedra, which in thin section show six-sided cross section. Sodalite is often anhedral in plutonic rocks. Symmetrically or zonally arranged inclusions are common in nosean and hauynite. Phenocrysts may be partially resorbed and have embayed edges.
Color: Colorless, gray, pale blue, bluish green to deep blue; the color may vary within a single crystal.
Pleochroism: –
Cleavage: –
Habit/Form: Crystals are dodecahedra, which in thin section show six-sided cross section. Sodalite is often anhedral in plutonic rocks. Symmetrically or zonally arranged inclusions are common in nosean and hauynite. Phenocrysts may be partially resorbed and have embayed edges.
Color: Colorless, gray, pale blue, bluish green to deep blue; the color may vary within a single crystal.
Pleochroism: –
Cleavage: –
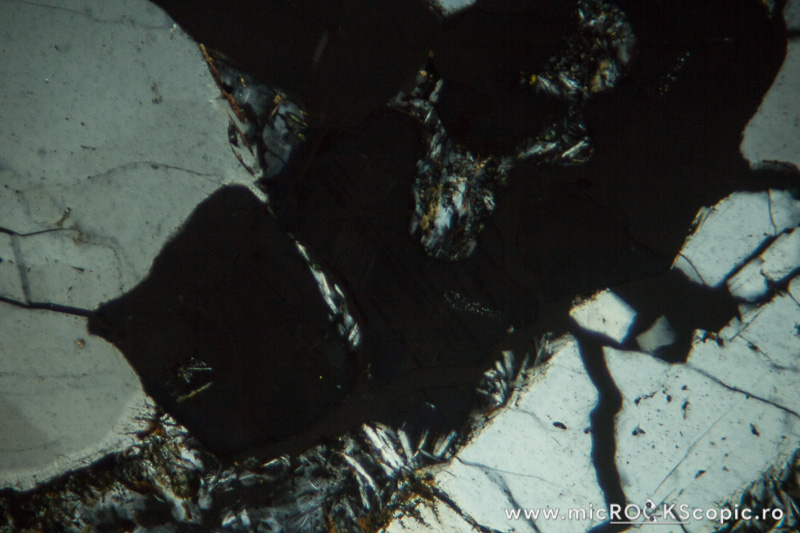
Hauynite XPL properties
Isotropy/Anisotropy: Isotropic; occasionally it may show very weak birefringence.
Interference color: Isotropic (black)
Extinction angle: –
Twins: Absent
Uniaxial/Biaxial: Isotropic (anomalous Biaxial)
Optic axial angle (2V): –
Interference color: Isotropic (black)
Extinction angle: –
Twins: Absent
Uniaxial/Biaxial: Isotropic (anomalous Biaxial)
Optic axial angle (2V): –
Hauynite distinguishing features under the microscope
Get Geology Toolkit Premium for more features of Hauynite thin section under the microscope.
References
- Deer, W. A., Howie, R. A., & Zussman, J. (2013). An introduction to the rock-forming minerals (pp. 498). Mineralogical Society of Great Britain and Ireland, London.
- mindat.org – The Mineral Database






![[thumb]](http://microckscopic.ro/wp-content/uploads/hauynite_1_01-1-150x150.jpg)
![[thumb]](http://microckscopic.ro/wp-content/uploads/hauynite_01-150x150.jpg)
![[thumb]](http://microckscopic.ro/wp-content/uploads/hauynite_06-150x150.jpg)






