About Nepheline
From Greek for cloud, because when the mineral is immersed in acid it becomes cloudy.
Nepheline hand-specimen
Formula: (Na,K)AlSiO4
System: Hexagonal
Color: White, grey, yellowish, greenish
Lustre: Vitreous, Greasy
Hardness: 5½–6
Density: 2.55–2.66
System: Hexagonal
Color: White, grey, yellowish, greenish
Lustre: Vitreous, Greasy
Hardness: 5½–6
Density: 2.55–2.66
Nepheline PPL properties
Relief: Low negative
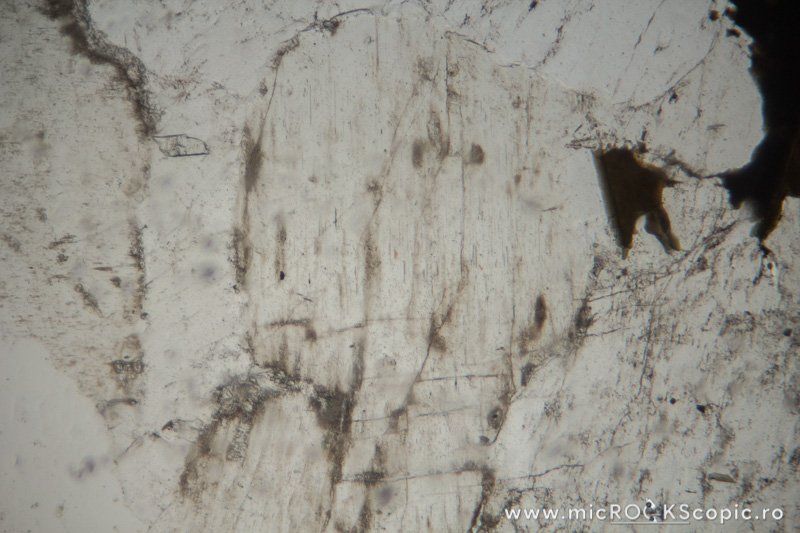
Habit/Form: In intrusive rocks, nepheline is usually anhedral or subhedral, and in volcanic rocks, it tends to form subhedral to euhedral crystals either as part of the groundmass or as phenocrysts. Crystals are usually stubby prisms with either a square or hexagonal cross section. Longitudinal sections are usually rectangular.
Color: Colorless (often cloudy). It may show rows of inclusions. Zonal structure may be due to arrangement of inclusions or to alternating layers richer and poorer in SiO2. Nepheline from young volcanic rocks are commonly comparatively clear, whereas those from plutonic rocks are usually turbid owing to pigment inclusions and/or alteration.
Pleochroism: –
Cleavage: Poor basal on {0001} and prismatic {10-10}; usually not seen in thin section
Habit/Form: In intrusive rocks, nepheline is usually anhedral or subhedral, and in volcanic rocks, it tends to form subhedral to euhedral crystals either as part of the groundmass or as phenocrysts. Crystals are usually stubby prisms with either a square or hexagonal cross section. Longitudinal sections are usually rectangular.
Color: Colorless (often cloudy). It may show rows of inclusions. Zonal structure may be due to arrangement of inclusions or to alternating layers richer and poorer in SiO2. Nepheline from young volcanic rocks are commonly comparatively clear, whereas those from plutonic rocks are usually turbid owing to pigment inclusions and/or alteration.
Pleochroism: –
Cleavage: Poor basal on {0001} and prismatic {10-10}; usually not seen in thin section
Nepheline XPL properties
Isotropy/Anisotropy: Anisotropic
Interference color: Order I gray to white; basal sections are dark.
Extinction angle: Rectangular longitudinal sections have parallel / 0° / straight extinction. Basal sections are dark between crossed nicols.
Twins: Rare
Uniaxial/Biaxial: Uniaxial (-)
Optic axial angle (2V): –
Interference color: Order I gray to white; basal sections are dark.
Extinction angle: Rectangular longitudinal sections have parallel / 0° / straight extinction. Basal sections are dark between crossed nicols.
Twins: Rare
Uniaxial/Biaxial: Uniaxial (-)
Optic axial angle (2V): –
Nepheline distinguishing features under the microscope
Get Geology Toolkit Premium for more features of Nepheline thin section under the microscope.
References
- Deer, W. A., Howie, R. A., & Zussman, J. (2013). An introduction to the rock-forming minerals (pp. 498). Mineralogical Society of Great Britain and Ireland, London.
- mindat.org – The Mineral Database














![[thumb]](http://microckscopic.ro/wp-content/uploads/nepheline_3_05-1-150x150.jpg)
![[thumb]](http://microckscopic.ro/wp-content/uploads/nepheline_4_04-150x150.jpg)
![[thumb]](http://microckscopic.ro/wp-content/uploads/nepheline_4_01-150x150.jpg)
![[thumb]](http://microckscopic.ro/wp-content/uploads/nepheline_2_05-150x150.jpg)
![[thumb]](http://microckscopic.ro/wp-content/uploads/nepheline_2_01-150x150.jpg)
![[thumb]](http://microckscopic.ro/wp-content/uploads/nepheline_6_05-150x150.jpg)
![[thumb]](http://microckscopic.ro/wp-content/uploads/nepheline_6_01-1-150x150.jpg)






