About Sillimanite
In the aluminosilicate group of isolated tetrahedral silicates, we include andalusite and kyanite for structural reasons, and sillimanite because of chemistry and polymorphism. The three polymorphs are among the most important minerals in pelitic schists, serving as indicators of relative pressure and temperature in metamorphic rocks. Named by George Thomas Bowen in honor of Benjamin Silliman (1779-1864), American chemist and geologist, Yale University.
Sillimanite hand-specimen
Formula: Al2SiO5
System: Orthorhombic
Color: Colorless, white, etc.
Lustre: Vitreous, Sub-Vitreous, Greasy
Hardness: 6½–7½
Density: 3.23–3.27
System: Orthorhombic
Color: Colorless, white, etc.
Lustre: Vitreous, Sub-Vitreous, Greasy
Hardness: 6½–7½
Density: 3.23–3.27
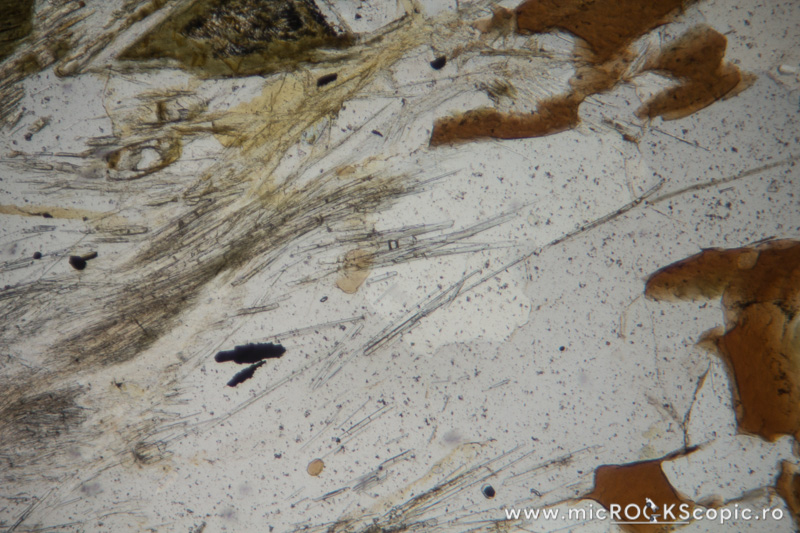
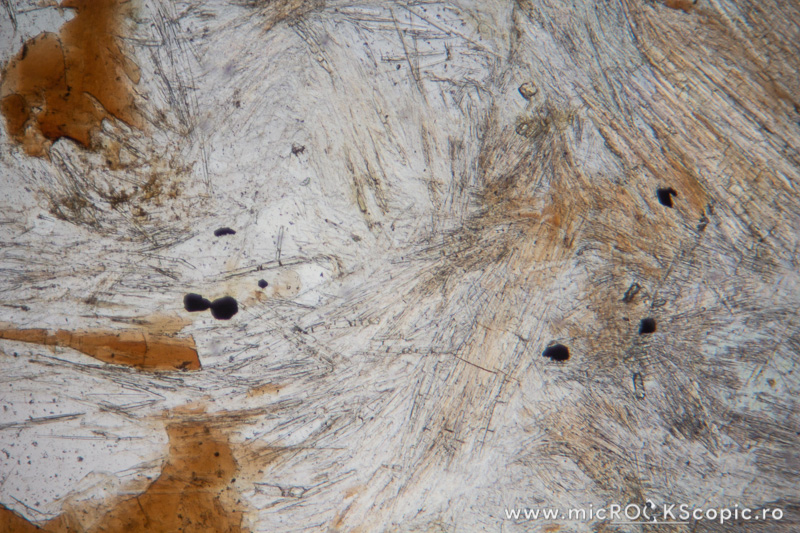
Sillimanite PPL properties
Relief: Moderate-High positive
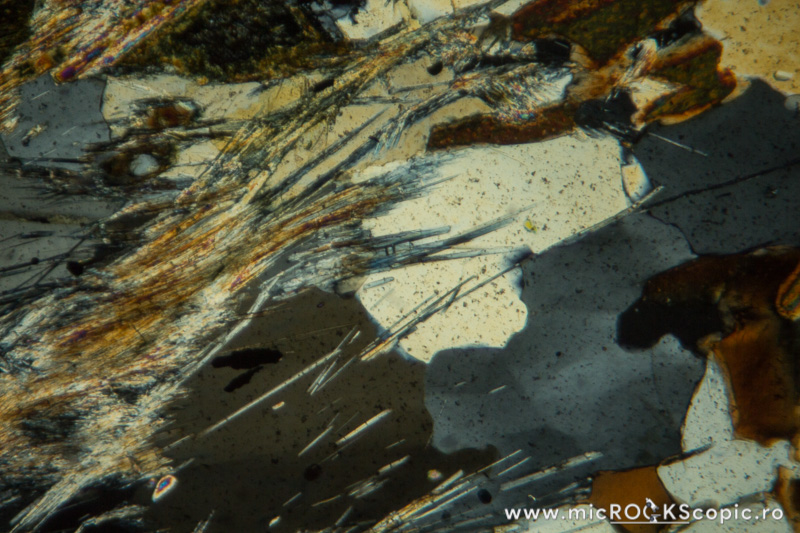
Habit/Form: Sillimanite commonly occurs as slender prismatic crystals or as fine fibrous crystals called fibrolite. Fibrolite commonly forms radiating, swirled, or matted aggregates. Cross sections through crystals are usually more or less diamond shaped.
Color: Usually is colorless; sometimes may be pale brown, pale yellow, brown, green, dark brown, blue
Pleochroism: None; sometimes weak to moderate
Cleavage: Parallel to {010} but not always noticed in sections. Transverse fractures are common.
Habit/Form: Sillimanite commonly occurs as slender prismatic crystals or as fine fibrous crystals called fibrolite. Fibrolite commonly forms radiating, swirled, or matted aggregates. Cross sections through crystals are usually more or less diamond shaped.
Color: Usually is colorless; sometimes may be pale brown, pale yellow, brown, green, dark brown, blue
Pleochroism: None; sometimes weak to moderate
Cleavage: Parallel to {010} but not always noticed in sections. Transverse fractures are common.
Sillimanite XPL properties
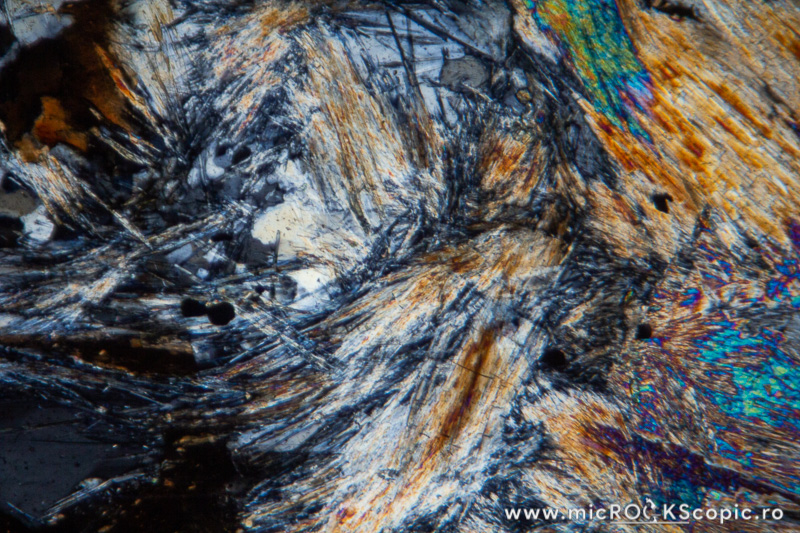
Isotropy/Anisotropy: Anisotropic
Interference color: Order I red to order II green; bright
Extinction angle: Parallel / 0° / straight in longitudinal sections and symmetrical in cross sections.
Twins: Absent
Uniaxial/Biaxial: Biaxial (+)
Optic axial angle (2V): 2V measured: 20 – 30°, calculated: 30 – 80°
Interference color: Order I red to order II green; bright
Extinction angle: Parallel / 0° / straight in longitudinal sections and symmetrical in cross sections.
Twins: Absent
Uniaxial/Biaxial: Biaxial (+)
Optic axial angle (2V): 2V measured: 20 – 30°, calculated: 30 – 80°
Sillimanite distinguishing features under the microscope
Get Geology Toolkit Premium for more features of Sillimanite thin section under the microscope.
References
- Deer, W. A., Howie, R. A., & Zussman, J. (2013). An introduction to the rock-forming minerals (pp. 498). Mineralogical Society of Great Britain and Ireland, London.
- mindat.org – The Mineral Database



![[thumb]](http://microckscopic.ro/wp-content/uploads/sillimanite_3_02-1-150x150.jpg)
![[thumb]](http://microckscopic.ro/wp-content/uploads/sillimanite_2_20-1-150x150.jpg)






